As blockchain technology advances, Starknet is leading the charge with its zk-rollup solutions. These innovative approaches are designed to overcome the limitations of traditional blockchain systems, paving the way for more efficient L2 solutions. The buzz is real, and it’s all about the STRK token airdrop, an event that’s causing a tidal wave of anticipation. Starknet, aspiring to be a decentralized, permissionless Layer 2 rollup, harnesses the power of zero-knowledge (ZK) technology. This technology offers a trifecta of benefits: massive scaling, swift transactions, and reduced costs, all while upholding Ethereum-level security.
So, whether you’re a developer, a blockchain enthusiast, or an investor keen on the economic nuances of tokenomics, particularly regarding the STRK token, this article aims to shed light on Starknet’s technical underpinnings and its approach to token unlocks, along with their implications.
The Genesis of StarkWare: A Fusion of Expert Minds
StarkWare Industries was founded in 2018 by a team of experts in cryptography, computer science, and engineering. The founding members are Uri Kolodny, Eli Ben-Sasson, Michael Riabzev, and Alessandro Chiesa, who have diverse expertise and backgrounds. The company’s mission is to solve scalability challenges and improve privacy and efficiency for blockchain networks. StarkWare raised $6 million in seed money and afterward $30 million in a series A round led by Paradigm. Other participants were Intel Capital, Sequoia Capital, Coinbase, and Vitalik Buterin. In March 2021, the company raised $75 million in a series B round. In May 2022, StarkWare raised $100 million in a Series D funding round, reaching an $8 billion valuation, up from the $2 billion valuation at its last fundraise.StarkWare’s STARK Technology: A Game Changer
StarkWare has significantly advanced blockchain scalability through the development of its STARK (Scalable Transparent ARgument of Knowledge) technology. Rooted in the principles of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs), STARKs are cryptographic proof systems designed for polylogarithmic verification resources and proof size, with an emphasis on minimal and post-quantum-secure assumptions.
Related: Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP): How It Works and Why Its Important
StarkWare’s implementation of ZK-STARKs has been a game-changer for blockchain integrity and privacy. These cryptographic proofs, backed by modern algebra, allow computations to be moved to an off-chain STARK prover and their integrity to be verified by an on-chain STARK verifier. This ZKP mechanism ensures that computation inputs remain undisclosed, thus enhancing user privacy. Only an off-chain prover that has executed the computation can generate STARK proofs, maintaining the integrity of the data.
STARKs contribute significantly to blockchain scalability by enabling off-chain computation and storage. Developers can relocate computational workloads off-chain, and the resulting STARK proofs verify the accuracy of these computations. Once these proofs are posted back on the blockchain, they can be verified by any interested party.
Comparative Analysis: STARKs vs. zk-SNARKs
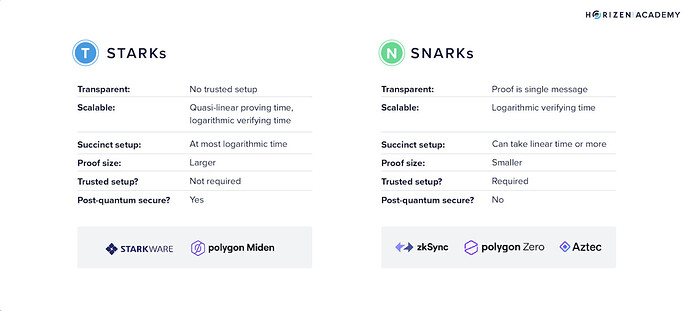
Understanding the difference between zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-interactive Argument of Knowledge) and zk-STARKs is crucial.Key differences include:
- Trusted Setup: zk-SNARKs require a trusted setup for initial parameters, posing a security risk. STARKs do not need such a setup, enhancing their security and transparency.
- Proof Size and Verification Time: While zk-SNARKs have smaller proofs and faster verification times, STARKs generate proofs more quickly and scale better.
- Quantum Resistance: STARKs are secure against quantum computer attacks, unlike zk-SNARKs.
- Transparency: STARKs are transparent, allowing anyone to verify the proof without access to secret information, which is not the case with zk-SNARKs.
- Scalability: STARKs are more scalable due to their simpler mathematical framework.
Cairo Programming Language: Bridging Efficiency and Safety
Cairo, a Turing-complete language designed by StarkWare, is instrumental in writing provable programs on Starknet. Drawing inspiration from Rust, Cairo is tailored for developing STARK-based smart contracts and Starknet OS, offering a safe and convenient programming environment.Features of Cairo
- Provable Programs: Cairo’s ability to generate STARK proofs of execution enhances trust and verifiability in blockchain applications.
- Efficiency: Designed for efficient proof generation, Cairo is key to blockchain scalability.
- Rust-Inspired Syntax: Cairo’s syntax, inspired by Rust, prioritizes performance, safety, and clear, maintainable code.
- Safety and Expressiveness: Cairo combines strong typing, ownership, and borrowing features, enhancing safety and expressiveness.
- Low-Level Access: It provides access to low-level memory and primitives for optimized code development.
- Stateful and Stateless Programs: It supports both stateful and stateless programming models.
StarkWare is actively developing Cairo with several upcoming upgrades, including new contract syntax, improvements to language constructs, the introduction of Sierra, and enhancements in syntax and type systems. While Cairo is a powerful language for building fast and scalable smart contracts, it is largely unsupported outside of the Starknet ecosystem .
Navigating the Growth of the Starknet Ecosystem
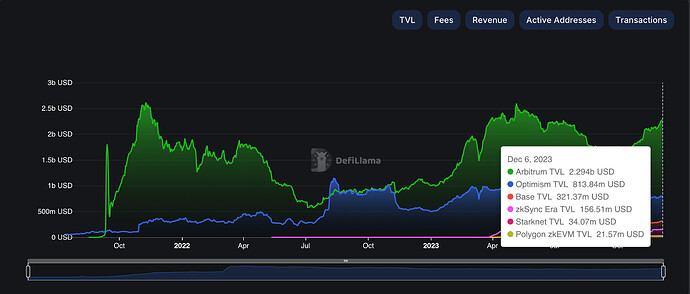
The Starknet ecosystem is a rapidly expanding network of developers, projects, and services built around Starknet. This ecosystem includes a wide range of components such as dApps, wallets, bridges, on-ramps, block explorers, indexers, full-nodes, RPC services, and security audits.As of the latest data, Starknet’s Total Value Locked (TVL) stands at approximately $32.82 million. Alongside this financial milestone, the ecosystem boasts 470,615 total transactions and a daily user count of 5,598.
A closer look at the top 5 protocols by TVL on Starknet reveals:
- mySwap (DEX) - TVL of $8.4 million.
- JediSwap (DEX) - TVL of $7.53 million.
- Ekubo (DEX) - TVL of $6.1 million.
- zkLend (Lending Protocol) - TVL of $4.97 million.
- 10KSwap (DEX) - TVL of $4.09 million.
Starknet in the Broader Context
While Starknet’s growth is noteworthy, it’s important to contextualize its position within the broader Layer 2 (L2) landscape. For comparison, as of November 2023, Arbitrum had a TVL of approximately $2.28 billion, and Optimism had a TVL of $783 million. In terms of user engagement, Base set a record as the fastest L2 to reach 100,000 users. These figures highlight Starknet’s potential areas for growth and its place in the competitive blockchain sector.
An Overview of STRK Token Distribution
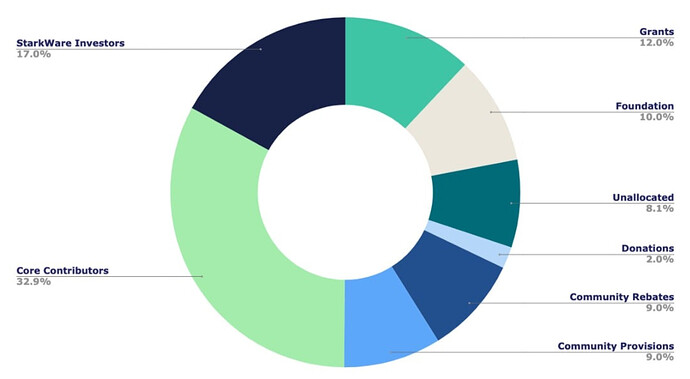
The Starknet (STRK) token is the native token of the Starknet ecosystem, a permissionless decentralized ZK-Rollup operating as a Layer 2 network over Ethereum. STRK token does not represent equity in StarkWare and does not grant any participation or claim rights in the company.The STRK token’s total supply stands at a staggering 10 billion, all minted off-chain by StarkWare. Let’s break down the allocation:
- Starkware Investors: 17% (1.7 billion STRK)
- Core Contributors: 32.9% (3.29 billion STRK), encompassing StarkWare’s team and software developer partners
- Starknet Foundation: 50.1% (5.01 billion STRK), further subdivided into various community and development funds, including a strategic reserve and provisions for donations and research. An intriguing 8.1% (810 million STRK) remains unallocated, hinting at future possibilities.
The tokens allocated to Core Contributors and Investors will be subject to a 4-year lock-up period, with linear release and a one-year cliff.
The STRK token will be used for governance, payment of transaction fees on Starknet, and participation in Starknet’s consensus mechanism. It will also serve as a staking token for participation in Starknet’s consensus mechanisms.
The Starknet token was launched on the Ethereum Mainnet in November 2022. However, as of the current date (December 6, 2023), the details of the Community Rebates and Community Provisions plans are yet to be determined. The Starknet Foundation is still developing plans to distribute the token to certain users, contributors, and investors.
Community Sentiment Around Starknet and Airdrop Speculations
The Starknet community presents a fascinating blend of enthusiasm and constructive criticism. Actively engaging on platforms like the Starknet Community Forum, Reddit, and Twitter, members are vocal about their experiences and expectations. For instance, while some users praise the network’s innovative features, others point out concerns regarding its speed, citing specific instances of transaction delays.
However, there are also positive sentiments, with discussions on growth and marketing strategies to drive Starknet’s user adoption, reflecting the community’s active involvement in the network’s development.
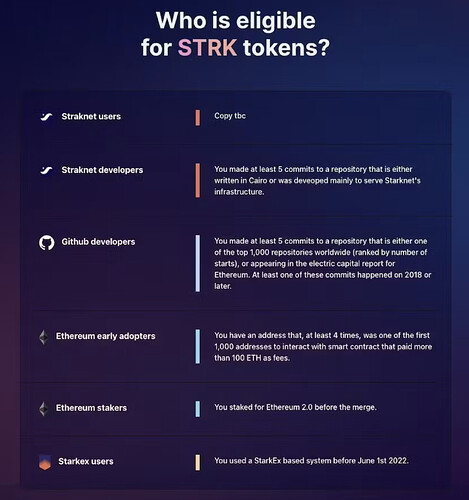
With 9% of the STRK supply allocated to end users and developers, the community is abuzz about the potential impact of this distribution. The snapshot for airdrop eligibility has been taken, sealing the fate of those who will partake in this event.
Starknet Developments in 2023 and Outlook for 2024: A Year of Growth and Future Decentralization
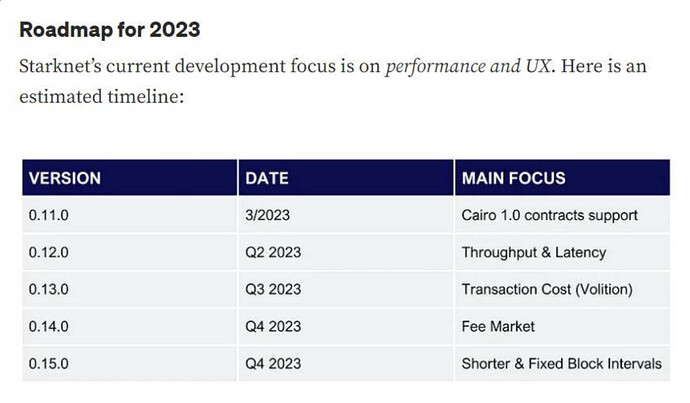
In 2023, Starknet made significant strides in enhancing user experience (UX) and network performance. The team focused on key areas such as usage efficiency, network throughput, latency, transaction costs, and speed. A milestone was the “Regenesis” phase, which involved seamlessly upgrading Cairo 0 smart contracts to Cairo 1.0, enhancing contract functionality without network disruptions.
The Starknet community witnessed remarkable growth in 2023, with its user base increasing eightfold over just two months. This surge was propelled by both the network’s enhanced capabilities and the growing interest in decentralized applications.
In 2024, the focus shifts to decentralizing operations and decision-making.
This involves:
- Decentralizing block production through its consensus protocol
- Decentralizing the proving layer responsible for computing proofs for blocks
- Decentralizing the process of L1 state updates
Starknet plans to introduce the STRK token in 2024 to facilitate decentralized governance, with the token introduction and airdrop scheduled for the same year.
Starknet’s Uphill Battle: Navigating Challenges Despite Advancements in ZK Technology and Growing User Base
Although Starknet is advancing zk technology through the integration of zkSTARKs and steadily building its user base, now generating excitement with its upcoming STRK token airdrop, the platform faces several critical challenges.
Transaction Fees: While Starknet’s fees are marginally cheaper than those of zkSync, they are not as competitive as other Layer-2 solutions or alternative Layer-1 chains.
Usage Complexity: The complexity of Starknet’s operations could pose difficulties for some users.
Lack of EVM Compatibility: Starknet does not offer full Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility, a feature available in Layer-2 solutions like zkSync and Optimism. This limitation requires developers to make substantial changes when migrating dApps from Ethereum Layer-1 to Starknet.
Programming Language: Despite being designed for developer ease, Cairo may be challenging for those accustomed to Solidity, Ethereum’s main programming language.
Competition: Starknet is in competition with various Layer-2 scaling solutions, such as zkSync, Polygon zkEVM, Optimism, ImmutableX, Arbitrum, and Aztec, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages.
Conclusion
2023 was a pivotal year for Starknet, marked by significant advancements in user experience (UX) and network performance. However, despite these developments and advancing the Zero Knowledge technology space with the invention of zkSTARKs, Starknet faces challenges such as lack of full Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility, and competition from other Layer-2 solutions.
Looking ahead to 2024, Starknet aims to further decentralize its operations, focusing on block production, the proving layer, and L1 state updates. A major development will be the introduction of the STRK token, set to drive decentralized governance and community participation, with an airdrop planned within the year.
And you can now keep pace with the developments of the STRK token using Token Unlock. Access crucial insights into STRK’s tokenomics, monitor vesting periods, and grasp the impact of token unlocks on the market. Stay informed and ahead - add the STRK token to your Token Unlock watchlist today for the latest updates and trends.